Fossil Fuels Pros and Cons
This list will be broken down based on the pros and cons associated with fossil fuels:
- Coal
- Oil
- Natural Gas
Pros of Coal

The following are the advantages associated with using coal:
It’s Available in Abundance
Not only is coal always available, but it is also stockpiled ready for immediate use. There is an estimated reserve of one trillion tons of coal. However the current reserves may not last until the end of the century. With that said, coal is a finite resource and is non-renewable on a human timescale.
Affordability
For homeowners, the cost of a ton of coal is affordable and provides weeks worth of heat.
Also, as it is mass-produced at a relatively low cost, those saving are passed on to the fuel that it produces.
It is accessible to virtually anyone as the cost equates to a few cents per kilowatt-hour.
Industry is Designed Around it
For more than 200 years homes and businesses have used coal to keep warm, steam locomotives have relied on it to move. Infrastructure has been designed around the knowledge that coal is a cheap, reliable, and efficient source of energy.
Readily Available
Renewable energy such as wind and solar power are both reliant on climate and sunlight. If they aren’t favorable then energy production draws to a halt, and expensive battery power has to be used to access any stored resources.
Coal is physical resource and is readily available when it’s needed. It can be mined, stored, and transported at times of high demand.
Improving Cleanliness
Along with soaring demand for coal comes new technology designed to massively reduce emissions. As coal combusts it emits gases that cause damage to the environment.
These technologies aid in the capture of the carbon and store it safely in order to limit potential damage.
Other Clean-Burning Methods
Coal can be converted to a liquid or gas. In such states, it burns inherently cleaner in its solid form, without losing any of its heating capacity.
Cons of Coal
There are also disadvantages of Coal to consider:
The Cost to Human Life
There have been multiple mining accidents over the years where countless miners have lost their lives.
Miners also suffer from lung and respiratory disease from the constant inhalation of coal dust. Among the mining community, it is known as Black Lung Disease.
Climate Change
Burning coal creates over 40% of the world’s carbon dioxide emissions and 72% of total Greenhouse Gases.
This accounts for rising global temperatures and has a detrimental effect on climate change.
Destruction of Habitats
Areas of mining are synonymous with the destruction of ecology and wildlife habitats. The removal of trees destroys the homes and feeding sources for many animals.
The groundwater within the region is likely to become polluted and underground mines carry a high risk of fire.
Once an area has been mined to capacity, there may be environmental toxins such as arsenic, sulfur dioxide, and mercury left behind.
Expensive
Employing clean coal technologies might be environmentally friendly but it is incredibly expensive to make the transition. An expense that will get passed on to the consumer. For example, changing coal-fired plants to use clean coal energy might see a 75% increase in the cost of fuel produced.
Finite Resource
Although coal is available in abundance, it is a fossil fuel, and will, at some point, run out.
Radiation
Coal-fired power plants emit low levels of radiation, but higher than any other fuel type. Sadly they are linked to higher rates of lung cancer and asthma in local areas.
Pros of Oil

The following are the advantages of using oil:
Cost-Effective
Centuries of innovation have enabled cheap energy production from oil consumption.
Our infrastructure is based on it; underground networks exist to easily transport liquid oil through pipelines covering large distances to isolated, rural areas.
Accessibility
It is an accessible fuel for everyone, almost every country in the world has access to an oil source.
It is comparatively cheaper than any non-renewable fuel, unlike wind and solar power. Oil is easy to store safely.
High Density
Oil is a substantial fuel, so much so that only a small amount is required for a large energy output.
For this reason, it is the main choice to power industrial machinery, planes, factories, and some vehicles.
It is essential for many industries including agriculture, automotive, clothing, and medicine.
Easy to Produce and Refine
Manufacturing oil is a simple process that has to adhere to strict industry regulations.
From drilling oil at source through to the refinement process is a meticulous systematic production line.
Aids Economic Growth
The oil industry supplements the economic growth of many countries.
Oil is relied upon to keep the machines running that make the most efficient machines easy to build.
This routine efficiency saves time, energy, and money.
The oil industry is responsible for mass employment down the food chain.
Cons of Oil
These are the cons associated with crude oil:
It’s Finite
Despite its many positive attributes, oil is an exhaustible resource and the supply will run out at some point.
Pollution
Nearly half of US carbon emissions and a third of global emissions are a result of oil burning, being drilled, and transported.
Oil combustion leads to methane and carbon dioxide being released into the atmosphere.
Not only are they major pollutants, but they also trap heat, making oil a major contributor to global warming.
The Threat to Wildlife and Mankind
Underground pipework is not infallible and prone to leakage. This results in pollution and the possible threat of explosion. Not only is this harmful to wildlife and habitats, but it also poses a huge risk to humans.
Oil Drill Disasters
Major incidents are not unheard of within the oil industry. The name Exxon Valdez is synonymous with the oil spill and the resultant catastrophic effect the oil slick had on the wildlife in 1989. Then there was the Deepwater Horizon disaster, the largest explosion, and oil spill known to man. Sadly, 11 oil workers lost their lives.
Acid Rain
Emissions created by and leaking from oil refineries create many issues. They are rich in pollutants such as sulfur dioxide which can create a health hazard to those in close populations.
When these pollutants combine with atmospheric water, acids are formed. Acid rain causes great environmental harm, particularly to forests and lakes. This creates many ecological knock-on effects as both are natural habitats.
Pros of Natural Gas
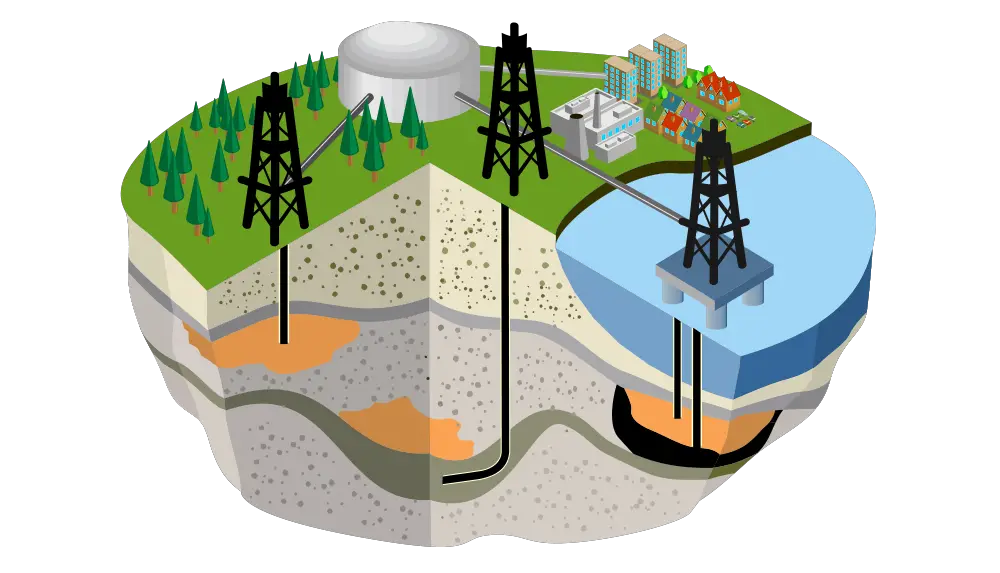

These are the advantages associated with natural gas:
Reduced Emissions
Of all fossil fuels, natural gas burns the cleanest. It emits 45% less carbon dioxide than coal and 30% less than oil.
Gas has a less adverse environmental impact.
Plentiful Supply
Although it is a finite resource, natural gas is available in abundance. There are more than 6879 trillion cubic feet available in the US.
It is thought that natural gas use will successfully replace coal and oil within 2 or 3 decades.
Safer Storage and Transportation
As the most efficient source of generating electricity and heating, it needs to be safe for domestic use. In its liquid form, it is safe to store above and below ground.
Transporting natural gas is done via the existing network of underground pipelines.
Above ground, it is common to use large ships and tankers to transfer gas around the country and beyond.
Cost-Effective
Globally, most engines require gas to run, as do many vehicles. As gas is so energy-efficient, they are cheaper to run.
Natural gas is also used for cooking and heating because it is an affordable energy source and releases less damaging emissions.
Oil-Producing Countries Can’t Hold Others Ransom
As gas is a reliable alternative to power vehicles and it can be used to generate electricity, gas makes countries almost self-sufficient.
It reduces their dependency on large oil-producing countries who can set their prices as they see fit.
Cons of Natural Gas
These are the disadvantages associated with Natural Gas:
Not Renewable
Natural gas is a fossil fuel and, as such, will release damaging emissions to some extent.
Although natural gas is available in plentiful supply, it is a finite resource. There will come a time when availability runs out, albeit a long way off.
Adds to the Greenhouse Effect
No matter in which circumstances gas is heated, whether it be for generating electricity, in the engine of a vehicle, cooking, or heating a home, harmful gases are released.
Carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides released into the atmosphere trap heat from the sun and contribute to global warming by raising the atmospheric temperature.
It is Highly Flammable
Natural gas is colorless and tasteless. You might be surprised to learn that it is also odorless. An odorant is added during refinement to aid detection.
Without it, gas leaks might go unnoticed; gas explosions can be catastrophic and cause a huge threat to life as well as the financial impact.
Environmental Consequences
Just like drilling for oil, hydraulic fracturing, fracking, is employed which cracks the seam of some rocks for extraction.
The highly pressurized liquid can contaminate drinking water in the region.
Also, as the rock has been weakened, earthquakes are more prevalent.
Expensive Transportation
Although it is easy to transfer natural gas from one place to another, the cost of the infrastructure is huge.
Due to its volatility, gas has to be moved in secure pipework and vehicles.