Solar inverters use a system of semi-conductors called IGBT – Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors. They are solid-state devices, that, when connected in the form of an H-Bridge, oscillate, converting DC to AC power.
Additional transformers enable power to transfer to and from the electricity grid.
If your solar array produces more power than your household requires, any excess funnels to the grid. Conversely, if your system doesn’t generate enough power, it can be topped up from the grid.
Overnight, an uninterrupted, consistent supply comes from the grid.
Types of Solar Inverter
There are three main types of inverters available; string inverters, string optimized inverters, and micro-inverters.
They all perform the same task, convert DC to AC, but their efficiency and price tag vary.
1. String Inverters
An inverter usually has 1 or 2 inputs, called MPPT, Maximum Power Point Tracker (more on these below).
Each line of panels connects via an independent string before joining the MPPT. Power runs through the strings continuously from the PV modules.
The output of the entire chain disrupts if any individual panel is affected by shade or bird droppings.
To Illustrate:
Imagine stepping on a hosepipe, water flow won’t only stop in the area you tread, but flow along the entire pipe is affected.
String inverter systems are efficient but not recommended in areas where trees, power cables, etc. regularly create shade.
2. String Optimized Inverters
The system works in a similar way to string inverters. However, each panel has a small optimizer on the back.
It enables the panels to be electrically independent of each other, therefore, if one unit is down the efficiency of the rest of the system isn’t disrupted.
Solar Edge optimized inverters provide a virtually unrivaled monitoring system, ensuring the owner is fully-aware aware of its productivity and consumption at all times.
3. Micro-Inverter
As the name suggests, micro-inverters are small devices that affix to the back of every individual solar panel. The direct current is converted at the panel, resulting in significantly higher output. Although the most expensive option, micro-inverters typically generate up to 15% more power than string systems.
They have no moving parts and are filled with polymers, making them dense and durable. Their life expectancy is 20+ years, they will last for as long as your solar panel provides maximum output.
Micro-inverters are premium systems that provide superb monitoring quality. The owner has the option of monitoring the system in its entirety or each panel individually if you want to remain on top of your electricity production and consumption statistics.
What is an MPPT?
Maximum Power Point Trackers are input channels found on string inverters. Their purpose is to maximize the available kinetic energy from solar panels strings during use.
Inverters without MPPT suffer when daylight and cell temperature conditions aren’t optimal, affecting the amount of energy harvested.
An MPPT closely monitors current and voltage, pushing the inverter to perform at its highest level at all times, therefore increasing the energy yield.
Single and dual MPPT inverters are available; the latter provides better system design flexibility and greater energy harvest.
Are Solar Inverters Expensive?
At an average cost of $0.70 per watt, the typical spend per application is $2,600. A high-end inverter increases power yield and therefore, quickly repays its cost.
Most systems only need one inverter; big industrial systems employ several.
For optimum performance match the inverter maximum output watts to the expected output of the array.
The Difference Between DC and AC Current
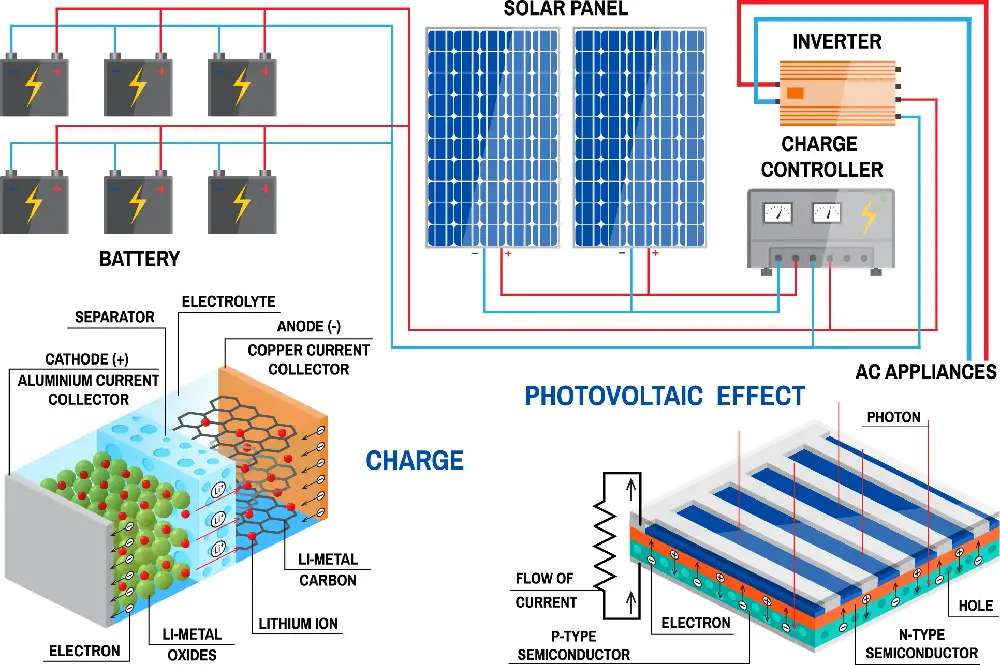
All commercial electronic appliances use AC power, Alternating Current.
It is the job of the solar inverter to convert DC power harvested from sunlight into AC electricity.
DC – Direct Current
Current flowing in one direction is direct, DC, and is the type of power supplied by solar cells and batteries.
For example:
A flashlight contains a continual electrical loop called a circuit that links the amp, battery, and switch. Electrical energy is systematically carried from bulb to battery until its energy runs out.
It is a typical example of an electronic device that uses DC; mobile phones and laptops are others.
A direct current shows as a straight line on an oscilloscope screen.
AC – Alternating Current
A current that constantly changes direction is alternating, AC, and is the type of power used by all commercial and domestic appliances.
It has a frequency of 50-60Hz (Hertz), equating to the number of times the current switches direction per second.
For example:
A cable leading from an outlet to a lamp is packed with electrons – you might wonder how they ever power the bulb if they’re forever changing direction?
When the power switches on, every electron vibrates back and forth rapidly, converting electrical energy into heat energy. This operation warms the filament, the bulb glows.
Unlike direct current, the electrons don’t need to transport energy in a continual circuit instead, they perform by jumping up and down in the same spot.




